What is Blockchain Technology and How Does it Work? Because of its technicality and nerdiness, the term “blockchain” is often misconstrued. Here is the ideal blockchain for dummies essay for you if you’ve been hearing this phrase tossed about with web 3.0 and crypto but aren’t quite sure what it means. Keep reading to get a basic understanding of blockchain technology, how it operates, its salient characteristics, pros and cons, and some practical applications.
What is Blockchain Technology in simple terms?
To put it simply, a blockchain is a distributed ledger that stores information in a decentralised format and is accessible from any computer with an internet connection.
Every node on the blockchain is connected because it uses P2P network technology. Every peer must authorize and record network transactions. This audits and records all transactions in all peers’ ledgers immediately after they join the network. This system is called “Distributed Ledger Technology”. Distributed ledger technology includes blockchain. Blockchain transactions are stored in blocks. A cryptographic hash links each block to the previous one. Since every peer has access to the same ledger and every alteration is immediately visible, changing one block without changing all blocks preceding it is nearly impossible. This creates a permanent block record that third parties cannot change. So, to put it simply, a blockchain is just a series of blocks. This method or technology records data as blocks that cannot be altered, hacked, or cheated.
What are the Key Features of a Blockchain?
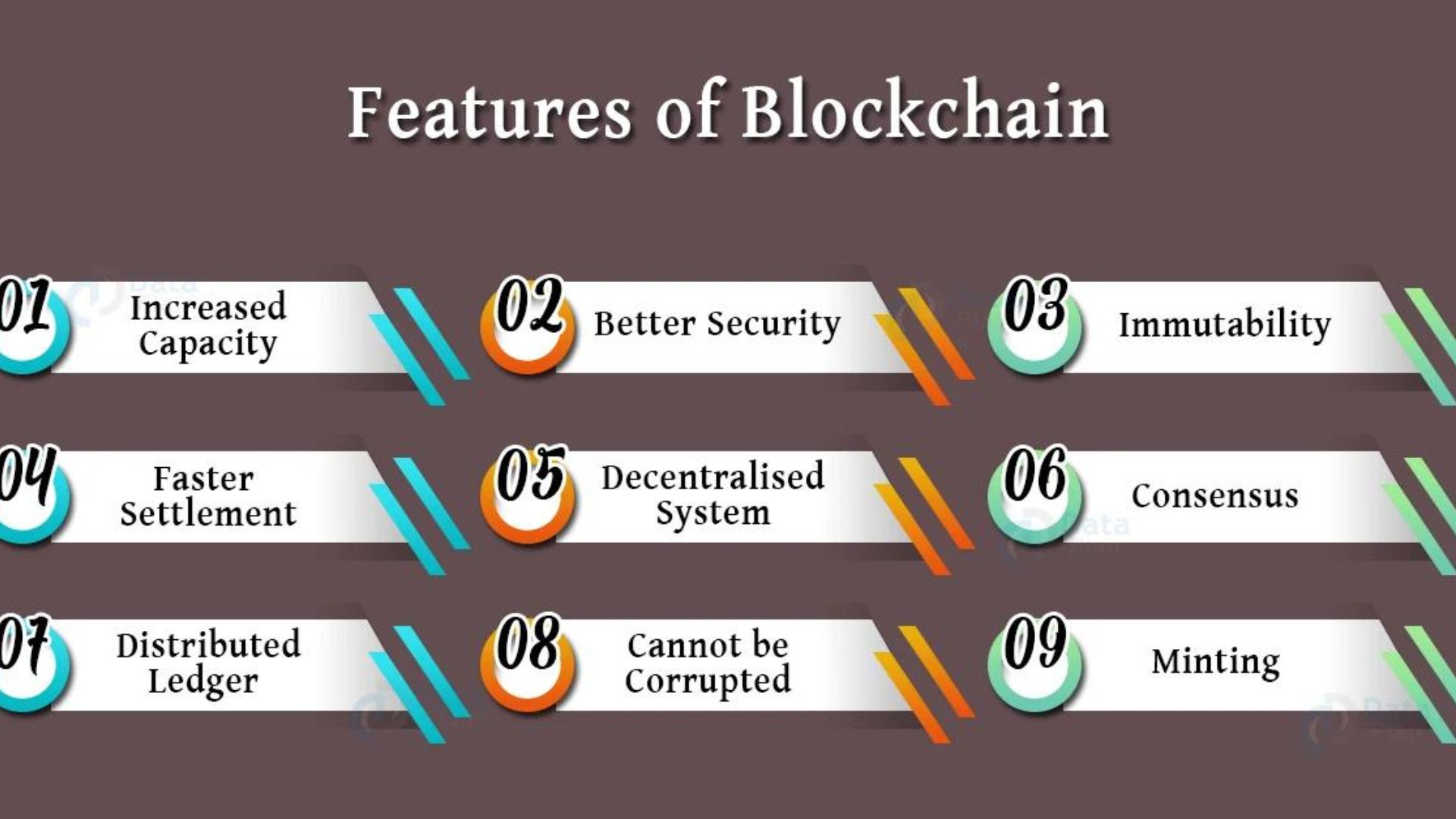
If you want to know how a blockchain works, there are a few things you need to know first.:
Immutability
The blockchain is permanent because it is immutable. It is impossible to change a block once it has been built.
Distribution
For the sake of transparency, every node (peer) in the blockchain network keeps a duplicate of the most up-to-date ledger. The present ledger and all network participants are fully disclosed in a public ledger. Within a decentralised ledger:
- Within minutes or seconds after verification, all modifications are reflected.
- Since there is a standardized procedure for adding blocks to a network, every node is equal.
Decentralization
Blockchain networks are decentralized because no single entity controls how the distributed ledger functions. Since computational power is used instead of human computations, the network is less likely to fail, and no third party is engaged.
Consensus
A blockchain network may reach a unanimous decision because it uses consensus. An algorithm for deciding decisions is a consensus. Therefore, the consensus that may make decisions for the network is trustworthy, even while peers do not trust each other.
Unanimity
Every node in the blockchain needs to be in agreement before adding a new block. Therefore, a majority vote is required before a peer can add a block to the network. The ledger is updated across all nodes in the network as soon as there is a unanimous vote to add the block.
Fast Settlement
Blockchains typically achieve settlement faster than conventional centralized systems due to their utilization of consensus procedures, computational capacity, unanimity, and decentralization in decision-making.
How does Blockchain Technology work?
The steps of adding a block to a blockchain network can be summarized in the following:
- A peer creates a new blockchain transaction using its computing power.
- The transaction is shared with all peers in the blockchain platform.
- All peers compute equations, validate the blockchain transaction, and can use consensus algorithms to come to a decision.
- Peers unanimously vote for the transaction to be included in a block.
- One block can cluster different transactions until it is full.
- A unique identifier containing a cryptographic hash of the current block, and the hash of the previous block is applied to the block.
- The block is added to the chain, and the ledger is updated across all peers.
The process of adding blocks to a blockchain network is called blockchain mining.
What are the Types of Blockchain Networks?
The permissions of each peer in the network further partition the underlying blockchain platform into the following blockchain networks:
- Public Blockchain Network
In a permission-less network, which is also known as a public blockchain, any peer can join in on the blockchain mining action. But the consensus algorithms must be followed by the peers.
- Private Blockchain Network
To manage who has access to what on a private blockchain network, businesses can use permissioned networks. What this means is that companies have the power to control who can and cannot mine blockchains. Some peers can also have access to certain data sets through the use of access control.
- Federated Blockchain Network
The consensus method in a federated blockchain network is managed by a group of nodes that have been chosen in advance. This type of network is also known as a consortium blockchain. What this means is that a small set of people have been hand-picked to oversee the blockchain mining process.
How does Blockchain Security work?

The blockchain platform is secure in three ways:
- Validation from all peers: Before any new block can be added to a blockchain, all of the nodes in the network must verify it. By distributing the real ledger among all remaining peers in the network, this decentralized procedure guarantees that no one can alter the data in any one peer, and any mismatch will be detected upfront. Therefore, to rephrase, there is no single point of failure in a blockchain network.
- Individual encryption: One more measure to ensure the security of a blockchain is the encryption of individual blocks. Each block has its unique identification because the applied encryption is a cryptographic hash. To solve the cryptographic hash of the block, every node in the network has a private key. This ensures that the peer network is alerted instantly in the event of a hash change, rendering the private key invalid. Additional harm is averted by this early warning.
- Chained to the previous block: In a blockchain, each block contains not only its own hash but also the hash of the block before it. It is physically impossible to edit a single block without also changing the hash of every other block; doing so would necessitate an enormous amount of processing power.
How did Blockchain Technology evolve?
Blockchain was initially proposed by Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta in 1991, but the concept is widely believed to have been developed by Satoshi Nakamoto, the anonymous creator of Bitcoin and another cryptocurrency built on the blockchain. After developing a cryptographically sound block chain, Haber and Stornetta enhanced their system in 1992 to include Merkle Trees. The anonymous creator of Bitcoin, Nakamoto, wrote a whitepaper outlining blockchain technology and gave control of the cryptocurrency to its core developers in 2009, however, only then did blockchain take off.
From 2012 to 2014, when Bitcoin first gained popularity, blockchain technology began to be utilized for financial transactions. Its first use was in smart contracts between 2014 and 2016, and since then, it has found more and more uses in the development of computer applications, particularly in the cryptocurrency industry.
What is the difference between a Database and a Blockchain?
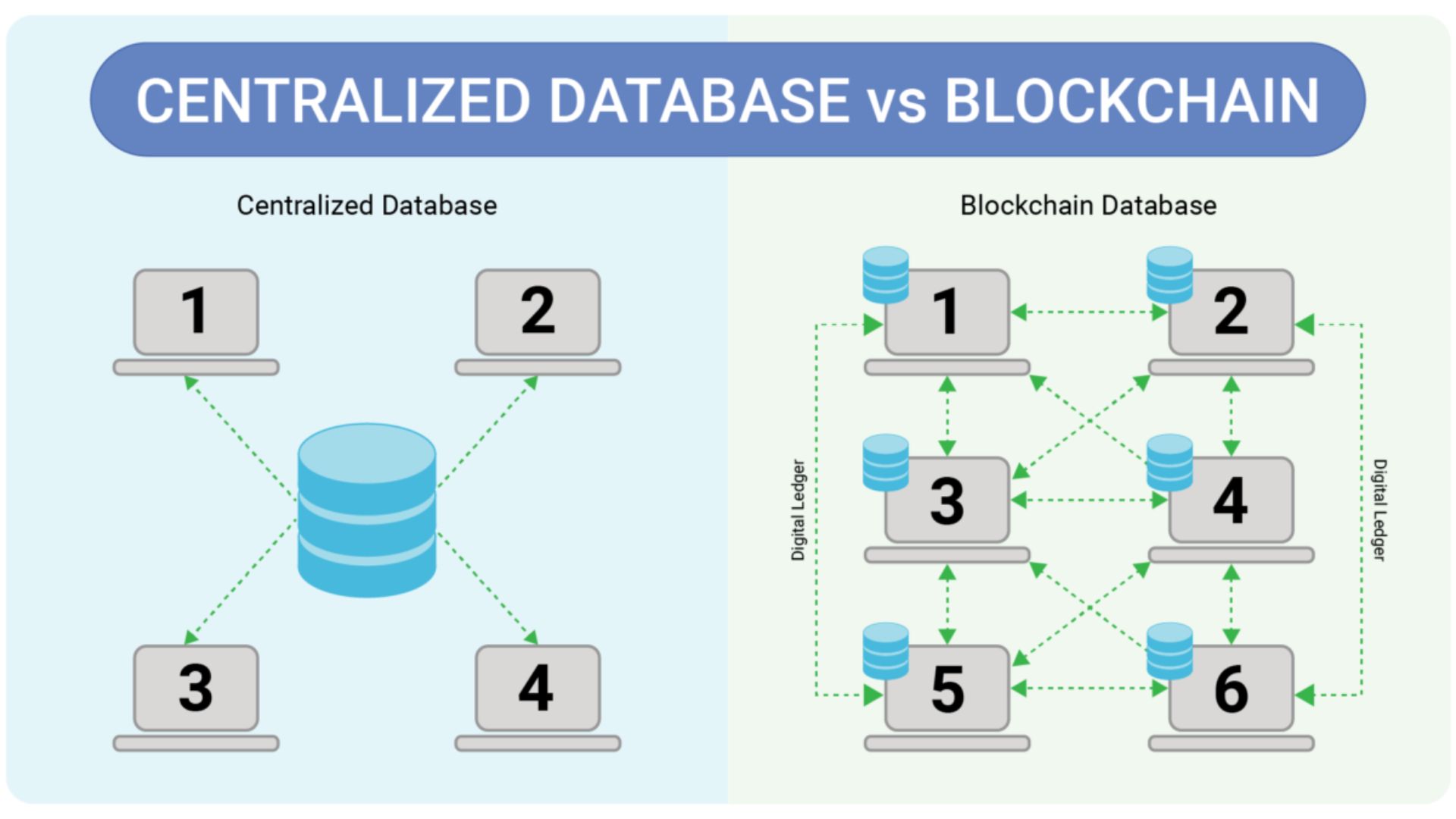
The term “database” refers to a collection of records kept by an administrator on a ledger. A database can only be viewed or written by those who have permission to do so. The definition highlights the key distinctions between blockchains and databases:
What problems does Blockchain technology solve?
Discovering what makes blockchain popular in real life is as vital as learning blockchain for beginners. Blockchain is a technical term with various practical uses that is gaining popularity:
Data Retention
Because everything is stored on all peers, distributed ledger technology (blockchain) is superior than putting critical data in a single, possibly susceptible location.
Government Operations
Biometrics and blockchain can improve government processes and identity management. Blockchains can improve taxation by confirming tax papers.
Crowdfunding
Blockchain aids crowdfunding. Blockchain ensures anonymous, global transactions, making funding safer, easier, and more transparent. This covers global crowdsourcing for any project.
Intellectual Property
Copyright or protect your intellectual property using blockchain if you produce a digital trail of blocks or records for it. This may be a music or a trade secret.
Data Protection
By utilizing distributed ledgers instead of centralized storage facilities, the security of sensitive cloud data can be significantly enhanced, thanks to the inherent security of blockchains.
Voting
Governments may protect voter identities by encrypting and saving every vote to the blockchain, which is hard to hack. This could eliminate electoral fraud.
Supply Chains
Supply chains benefit from blockchain. Recording every product’s supply chain trip speeds blockchain registration, connection, sharing, assignment, and tracking. Unethical and illicit wealth transfer may be less.
Bypassing Intermediaries
Transactions can avoid middlemen with blockchain technology since it is a decentralised network of peers. This way, no third parties need to know any sensitive information in order to complete the transaction.
Financial Transactions/ Cryptocurrency
The blockchain supports financial transactions. Banks accept most payments. Blockchain lets bitcoin borrowers and lenders use them safely, quickly, and efficiently. This makes blockchain transactions cheaper than banks.
Charity
Blockchains can also make philanthropic donations public and reveal their usage. This can transform the charity industry if stakeholders believe in it.
Are there any disadvantages of Blockchain Technology?
This article discusses blockchain technology’s security, transparency, instant traceability, efficiency, and automation. However, consider the technology’s drawbacks:
Slowed down process
While blockchains are speedier by design, an excessive number of users could cause them to stutter.
Scalability issues
One of the challenges with blockchains is their inability to scale due to network congestion and consensus algorithms.
Inefficient
Blockchains aren’t always efficient because they have the ability to use a lot of power. Using private blockchain networks rather than public ones can help mitigate the issue, but it won’t fix it entirely.
Immutability can be an issue
When someone wishes to have their data erased from the network, immutability becomes a problem with blockchains. For some, this may constitute an invasion of privacy.
Not completely secure
Blockchain is more secure than traditional networks, however a 51% assault compromises security if one party controls more than 51% of the network. DDoS attacks and cryptographic cracking (due to insecure encryption) are further blockchain dangers.
Irrecoverable Keys
Private keys can crack block cryptographic hashes. If they lose the private key, they can never access the system. Because peers and users have different technical knowledge, issues may develop.
Costly
Both the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs of blockchain implementation are substantial.
Knowledge Requirement
Participating in a blockchain network necessitates technical expertise and appropriate education, neither of which are usually readily available.
Interoperability issues
Interoperability concerns arise when traditional systems utilize blockchain technology because most blockchains have their own algorithms and tackle problems in their own way.
Conclusion
Lastly, blockchain networks are currently experiencing a surge in popularity. The technology’s security, increased visibility, traceability, and verification efficiencies make up for its drawbacks, which are driving up its usage.
Since the blockchain appears to be only going to grow in popularity in the years ahead, it is crucial for tech savvy people to familiarize themselves with it now.


